Ransomware Prevention: Strategies to Protect Your Data from Attackers
Ransomware attacks have surged in recent years, targeting individuals and organizations alike with devastating consequences. Cybercriminals use this malicious software to encrypt victims’ data, demanding a ransom for its release. As these attacks become increasingly sophisticated, it is essential for businesses and individuals to adopt proactive strategies for ransomware prevention. This article outlines effective measures to safeguard your data from ransomware threats.
Understanding Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malware that restricts access to a computer system or files until a ransom is paid. Attackers typically exploit vulnerabilities in software, utilize phishing tactics, or leverage unsecured networks to infiltrate systems. The impact of a ransomware attack can be catastrophic, leading to financial loss, data breaches, and reputational damage. Prevention is key, and organizations must take a comprehensive approach to protect themselves.
Strategies for Ransomware Prevention
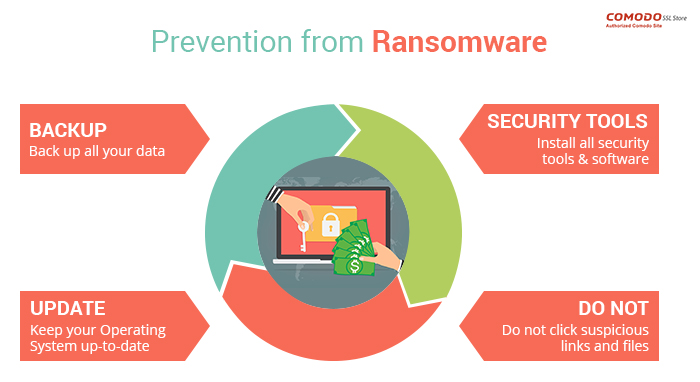
1. Regular Backups
One of the most effective defenses against ransomware is maintaining regular backups of critical data. By implementing a robust backup strategy, you can ensure that, in the event of an attack, you can restore your data without paying the ransom. Consider the following backup practices:
- Automate Backups: Schedule regular backups to minimize the risk of data loss.
- Use Multiple Locations: Store backups both on-site and in the cloud to enhance redundancy.
- Test Backup Restorations: Periodically test your backup restoration process to ensure that data can be recovered quickly and effectively.
2. Keep Software Updated
Cybercriminals often exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software. To mitigate this risk, organizations must:
- Regularly Update Systems: Ensure that all operating systems, applications, and security software are updated promptly to patch known vulnerabilities.
- Enable Automatic Updates: Where possible, enable automatic updates to streamline the process and reduce the likelihood of human error.
3. Implement Strong Security Measures
Employing robust security measures is essential in defending against ransomware attacks. Consider the following strategies:
- Use Firewalls and Antivirus Software: Implement firewalls to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic. Complement this with reputable antivirus software to detect and block malware.
- Utilize Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Deploy IDS to monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and respond promptly to potential threats.
4. Educate Employees
Human error remains one of the most significant vulnerabilities in cybersecurity. To bolster your defenses:
- Provide Cybersecurity Training: Educate employees about ransomware threats, phishing tactics, and safe online practices. Training should be ongoing to keep security awareness top of mind.
- Simulate Phishing Attacks: Conduct regular phishing simulations to help employees recognize suspicious emails and improve their response to potential threats.
5. Restrict User Access
Implementing the principle of least privilege ensures that users have only the access necessary to perform their roles. This limits the potential damage caused by a compromised account. To enhance access control:
- Create Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC): Assign permissions based on user roles, minimizing unnecessary access to sensitive data.
- Regularly Review Access Rights: Conduct periodic audits to ensure that access permissions remain appropriate as roles and responsibilities change.
6. Establish an Incident Response Plan
Having a well-defined incident response plan is crucial for minimizing the impact of a ransomware attack. This plan should include:
- Detection and Analysis: Outline procedures for identifying and assessing ransomware incidents.
- Containment and Eradication: Define steps for containing the attack and eradicating the ransomware from affected systems.
- Recovery and Post-Incident Review: Detail processes for data recovery and conducting a post-incident analysis to improve future defenses.
Conclusion
Ransomware attacks pose a significant threat to individuals and organizations, but proactive measures can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to such attacks. By implementing regular backups, keeping software updated, strengthening security measures, educating employees, restricting user access, and establishing a comprehensive incident response plan, you can protect your data from attackers. In a landscape where cyber threats are ever-evolving, a proactive and layered approach to ransomware prevention is essential for safeguarding your valuable information and maintaining business continuity.