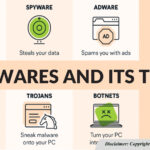
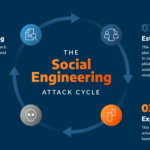
Essential Cybersecurity Practices for Protecting Your Business from Threats
In today’s digital landscape, cybersecurity has become a top priority for businesses of all sizes. As organizations increasingly rely on technology to operate, the risks associated with cyber threats—such as data breaches, ransomware, and phishing attacks—continue to grow. Protecting sensitive information and maintaining trust with clients and stakeholders is crucial. This article outlines essential cybersecurity practices that businesses can adopt to safeguard their operations against emerging threats.
1. Conduct Regular Risk Assessments
The first step in developing a robust cybersecurity strategy is understanding the specific risks your business faces. Conducting regular risk assessments helps identify vulnerabilities within your systems, processes, and personnel. This proactive approach allows organizations to prioritize resources effectively and implement targeted security measures. Key aspects to evaluate include:
- Data Sensitivity: Determine the types of data your business handles and assess their sensitivity.
- System Vulnerabilities: Identify outdated software or hardware that may expose your organization to threats.
- User Behavior: Analyze employee practices that could lead to security breaches.
2. Implement Strong Password Policies
Weak passwords are one of the most common vulnerabilities that cybercriminals exploit. To mitigate this risk, businesses should establish strong password policies that encourage secure practices, including:
- Complexity Requirements: Mandate the use of long, complex passwords that include a mix of letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Regular Updates: Require employees to change their passwords periodically, reducing the likelihood of unauthorized access.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA to add an extra layer of security, requiring users to provide additional verification beyond just a password.
3. Train Employees on Cybersecurity Awareness
Human error is often the weakest link in cybersecurity. Providing employees with regular training on cybersecurity best practices can significantly reduce the risk of security breaches. Key topics to cover in training sessions include:
- Phishing Awareness: Teach employees to recognize and report phishing emails or messages that may attempt to steal sensitive information.
- Safe Internet Practices: Encourage safe browsing habits, including avoiding suspicious websites and downloads.
- Social Engineering Tactics: Inform employees about various social engineering techniques that cybercriminals may use to manipulate them into divulging confidential information.
4. Keep Software and Systems Updated
Regularly updating software, operating systems, and applications is vital for maintaining security. Software updates often include patches that address vulnerabilities exploited by cybercriminals. Businesses should:
- Automate Updates: Enable automatic updates whenever possible to ensure systems are always running the latest security patches.
- Inventory Software: Maintain an inventory of all software and systems in use, making it easier to track which ones need updates.
5. Establish a Data Backup Plan
Data loss can occur due to various reasons, including cyberattacks, hardware failures, or natural disasters. Establishing a robust data backup plan ensures that critical information can be restored in the event of a breach or loss. Consider the following best practices:
- Regular Backups: Schedule regular backups of all important data, ensuring that both on-site and cloud-based solutions are utilized.
- Test Restores: Regularly test data restoration processes to ensure backups can be successfully recovered when needed.
6. Implement Network Security Measures
Securing the network infrastructure is critical for protecting business data. Organizations should adopt the following network security measures:
- Firewalls: Utilize firewalls to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic, blocking unauthorized access.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Implement IDS to detect and respond to suspicious activity in real-time.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPN): Use VPNs to secure remote connections and protect sensitive data transmitted over the internet.
Conclusion
As cyber threats continue to evolve, businesses must remain vigilant in their cybersecurity efforts. By implementing essential practices such as regular risk assessments, strong password policies, employee training, software updates, data backups, and network security measures, organizations can significantly enhance their defenses against cyberattacks. Prioritizing cybersecurity not only protects sensitive information but also fosters trust among clients and stakeholders, ultimately contributing to long-term business success. In a world where cyber threats are omnipresent, taking proactive steps to safeguard your business is not just a choice; it is a necessity.